Power Supply Unit (PSU)
PSUs are an essential part of any computer or electronic device. Without a PSU, the device would not be able to power on or function. There are two main types of PSUs: switching and linear. Switching PSUs are more efficient than linear PSUs, and they are the most common type of PSU used in computers. Linear PSUs are less efficient, but they are also less expensive.

Corsair RM850x 850W 80+ Gold Certified
This is an example of good PSU, from Corsair, a well-known manufacturer of computer hardware. It is a 850W PSU, which means that it can provide up to 850 watts of power to the components of a computer. Most computers these days are compatible with this PSU. It can supply power for 2 video cards easly.
Selection Factors
Here are some of the factors to consider when choosing a PSU:
- Wattage rating: The wattage rating of a PSU determines how much power it can provide to the components of a computer.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of a PSU determines how much of the power from the electrical outlet is converted into DC power that is used by the components of a computer.
- Form factor: The form factor of a PSU determines the size and shape of the PSU.
- Modularity: Modular PSUs allow users to connect only the cables that they need, which can help to reduce clutter inside a computer case.
- Location: There are significant differences between power connectors in different continents and countries. Make sure you selected PSU is usable
When you chose a PSU first thing you nee to know is what motherboard, proesor an video card you are going to use. You must calculate total power requirements and add a rezerve of 25% more than you need. Second, is the form factor of the computer case. If the computer case is small, be aware some power supply units are very large and may not fit inside the computer case. That would be a failed investmant, do your research properly to avoid leaking money.
Power Supply Unit (PSU) Connectors
Power supply units (PSUs) use a variety of connectors to deliver power to the components of a computer. The most common types of PSU connectors are:
| 24-pin ATX connector | This connector is used to provide power to the motherboard. |
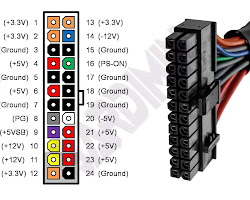
|
| 8-pin EPS12V connector | This connector is used to provide power to the CPU. |

|
| 6-pin PCIe connector | This connector is used to provide p.ower to graphics cards. |

|
| 4-pin Molex connector | This connector is used to provide power to older devices, such as hard drives and optical drives. |
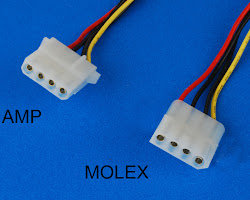
|
| SATA connector | This connector is used to provide power to SATA hard drives and optical drives. |

|
PSU connectors come in a variety of colors, which can help to identify the type of connector. For example, 24-pin ATX connectors are typically black, 8-pin EPS12V connectors are typically yellow, 6-pin PCIe connectors are typically red, and 4-pin Molex connectors are typically blue.
It is important to use the correct type of connector for each component. Using the wrong type of connector can damage the component or the PSU. Sometimes the connectors are just not matching the components. Then you must use an adaptor.
Modular Power Supply Unit (PSU)
A modular power supply unit (PSU) is a type of PSU that has detachable cables. This means that you only connect the cables that you need, which can help to reduce clutter inside a computer case. Non-modular PSUs, on the other hand, have all of the cables permanently attached. This can make cable management more difficult, especially in small cases.
Modular PSUs are typically more expensive than non-modular PSUs, but they can be a good option if you are looking for a clean and organized build. Here are some of the benefits of using a modular PSU:
- Clutter reduction: Modular PSUs allow you to only connect the cables that you need, which can help to reduce clutter inside a computer case. This can make it easier to see the components inside your case and to access them for maintenance. [Image of Clutter reduction with modular PSU] Better cable management: Modular PSUs give you more control over the routing of your cables, which can help to improve the airflow inside your case. This can lead to better cooling performance and can help to prevent your components from overheating.
- Easier upgrades: If you need to upgrade your PSU in the future, it will be easier to do with a modular PSU. You can simply remove the cables that you don't need and install the new PSU.
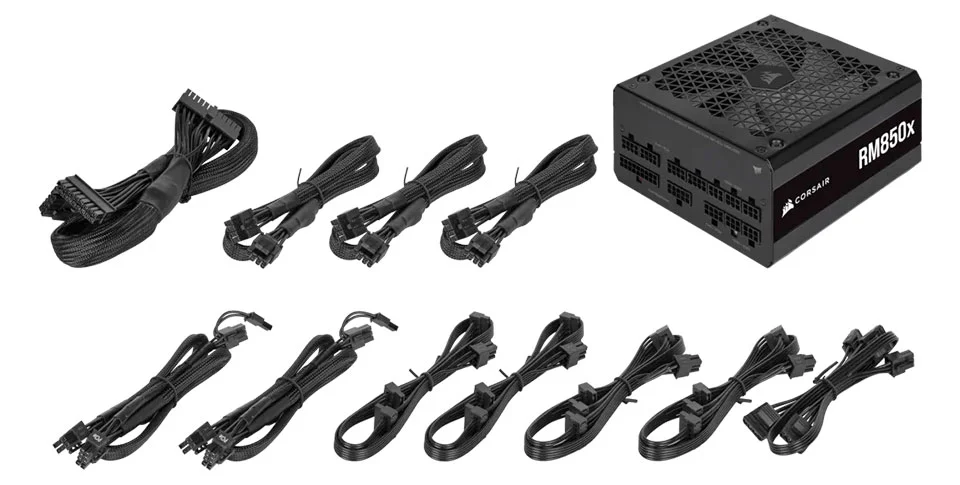

Modular PSU with all the cables
Overall, modular PSUs offer a number of benefits over non-modular PSUs. However, they are also more expensive and can be more complex to install. If you are looking for a clean and organized build, a modular PSU is a good option. However, if you are on a budget or if you are not concerned about cable management, a non-modular PSU may be a better choice.
(PSU) Power Requirements
When choosing a power supply unit (PSU) for your computer, it is important to calculate the power requirements of your components. This will help you to ensure that you choose a PSU that is powerful enough to meet the needs of your system.
There are a few different ways to calculate power requirements for a PSU. One way is to use a power supply calculator. There are a number of different power supply calculators available online, such as the one at Outervision.
Another way to calculate power requirements for a PSU is to manually add up the power consumption of each of your components. You can find the power consumption of each component in the product specifications.
Once you have calculated the power requirements for your components, you need to add a bit of headroom. This will ensure that you have enough power to accommodate any future upgrades that you may make to your system.
A good rule of thumb is to add 20% to the calculated power requirements. For example, if your calculated power requirements are 500 watts, you should choose a PSU that is at least 600 watts.
Here are some of the factors that you should consider when calculating power requirements for a PSU:
- The type of CPU: The power consumption of a CPU can vary depending on the type of CPU and the settings that you use.
- The type of graphics card: The power consumption of a graphics card can vary depending on the type of graphics card and the settings that you use.
- The number of hard drives and other storage devices: Hard drives and other storage devices typically consume a small amount of power.
- The number of fans: Fans typically consume a small amount of power.
Power Supply Units (PSUs) in Different Countries
Power supply units (PSUs) are used in computers all over the world, but the voltage and amperage requirements can vary depending on the country. Here is a table of the different voltage and amperage requirements for PSUs in different countries:
| Country | Voltage | Amperage |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 120 volts | 60 amps |
| Europe | 220 volts | 50 amps |
| United Kingdom | 230 volts | 50 amps |
| Australia | 240 volts | 50 amps |
| Japan | 100 volts | 50 amps |
| China | 220 volts | 50 amps |
It is also important to note that the power outlets in different countries can have different shapes. For example, the power outlets in the United States have two flat prongs, while the power outlets in Europe have two round prongs. If you are traveling with a computer, you will need to make sure that the power cord is compatible with the power outlets in the country that you are visiting.
| Power Cord Type | Country |
|---|---|
| IEC 60320 C13/C14 | Most countries |
| Type A | United States, Canada |
| Type B | United States, Canada |
| Type C | Most European countries |
| Type E | France, Belgium, etc. |
| Type F | Germany, Switzerland, etc. |

Power Outlet
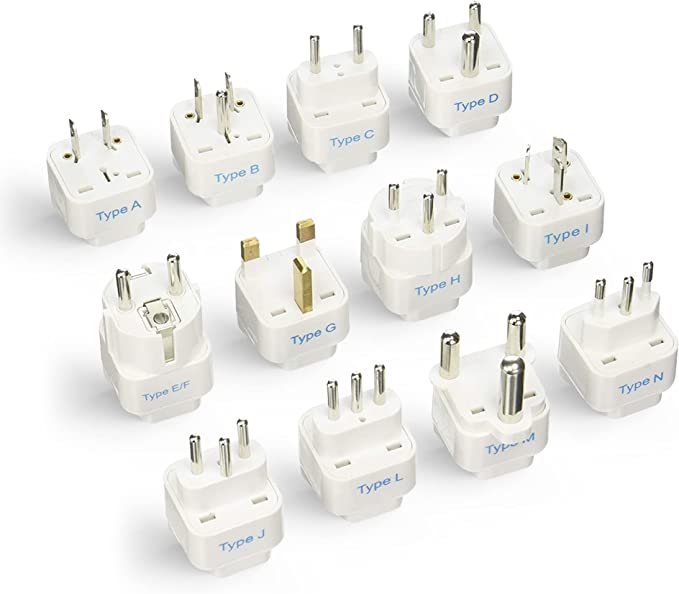

Power Plug
If you are not sure what voltage and amperage requirements your PSU needs, you can usually find this information in the product specifications. You can also contact the manufacturer of your PSU for more information.
Read next: Magnetic Disk
