Magnetic Disk
Page bookmarks
What is a HDD?
These devices are very successful due to rapid access to read or write information. These devices are designed for desktop PC, Servers or Laptops. In the next picture you can study the internal components of a HDD but the real HDD is encapsulated in a case, for protection. You should never open a HDD, even if is broken.
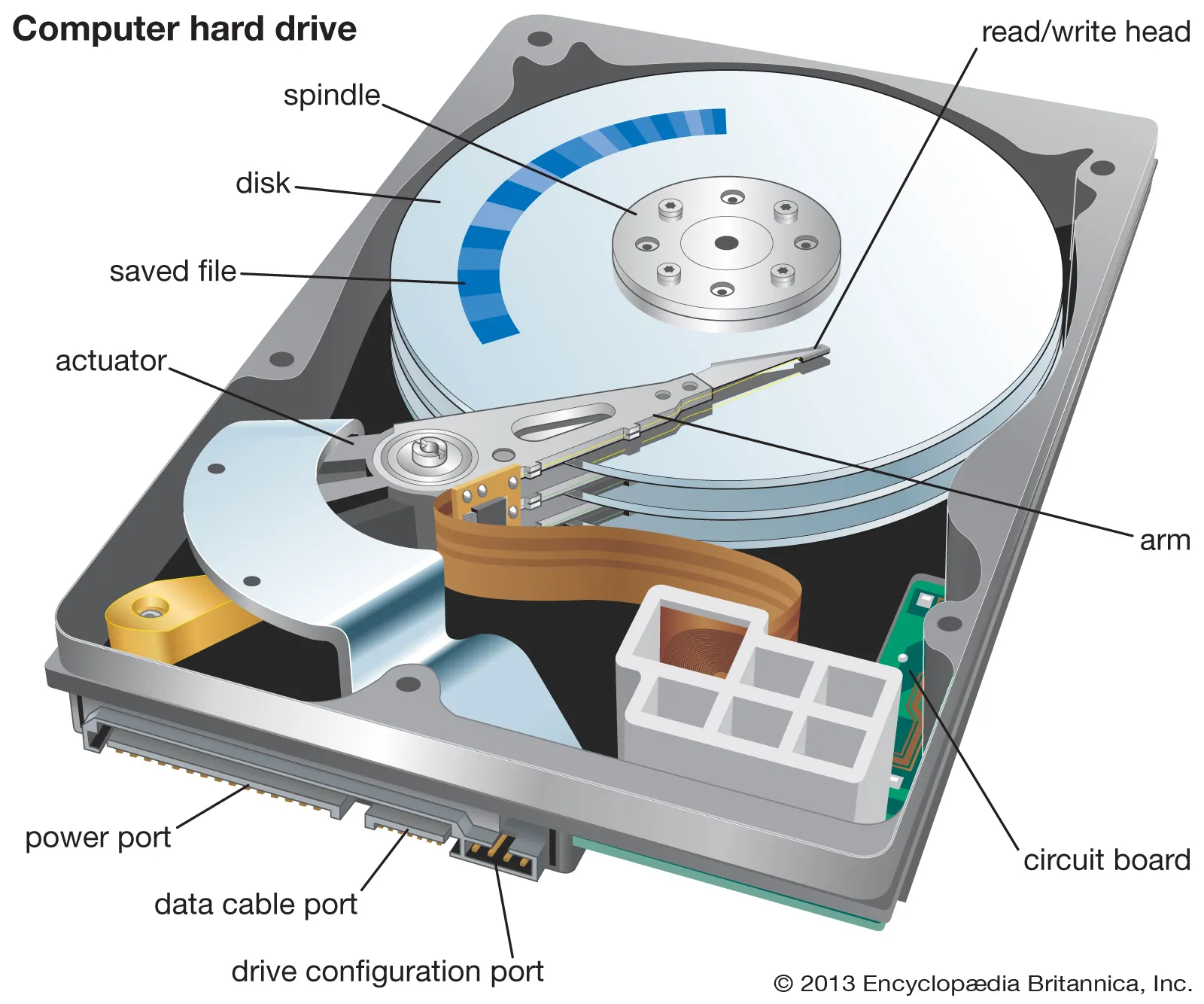
Hard Disk Anatomy
Technology: these devices are using one or several disk platters that are mounted on a spindle. The patters are easy to magnetize and demagnetize using a small coil mounted on a moving head that is reading or writing data. Some HDD are using a single disk some other are using one 2 or 3 platters on the same axis but new disks can have upt to 8 platters to increase the capacity.
Performance: Depending on the number of disks mounted on the spindle and depending on the rotation speed, the HDD can be faster or slower. The spinning is measured in RPM (rotation per minute). For example a 15000 RPM or 10.000 RPM is used for fast responsive server side HDD while 7500 RPM is used for desktop computer while 5000 RPM disks are used for laptop computers.
Capacity: The capacity of HDD is measured in GB (GigaByte) or TB (TeraByte). Usually a laptop is using a single HDD of small capacity (GB) while desktop or servers can use 2 or more HDD of large capacity (TB). Today you can find HDD of large capacity between 250Gb to 1TB for a dektop computer and up to 22TB for a server.
Desadvantages: Because HDD has moving parts it generate heat, vibrations and is subject to mechanical and thermal degradation. Also a HDD can produce noize. Therefore for a silent home computer we preffer to use M2 NVMe or SSD. You can use HDD for a home computer, game computer or home server. Usually HDD is used for enterprise computers.
HDD Connectors
Hard disk drives (HDDs) use two types of connectors: power connectors and data connectors.The power connector is used to provide power to the HDD. It is typicmlly a 4-pin Molex connector, but some newer HDDs may use a SATA power connector.
The data connector is used to transfer data between the HDD and the computer. It is typically a SATA connector, but some older HDDs may use an IDE connectors. Older servers have SCSI connectors. New servers can use SAS connectors.
Here is a table showing the different types of HDD connectors:
| Connector Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Connector | Provides power to the HDD. |
| SATA Connector | Transfers data between the HDD and the computer. |
| IDE Connector | Older type of data connector that is no longer commonly used. |
| SAS Connector | Serial Attached SCSI connector. Provides higher transfer speeds than SATA. |
| SCSI Connector | Small Computer System Interface connector. Older type of connector that is no longer commonly used. |
SATA Connectors
In the picture below we have a SATA hdd. The electronic bord has 2 connectors, one is the SATA Power, the other one is the SATA data cable. You need to install the cable in the correct port, but you can't do mistakes because the port has a L shape, and is full-proved:

Sata Cable
MOLEX Adapter
Power supply has special cables to provide SATA Power. An older power suply may provide power for older HDD that is PATA standard. In this case, you need and adaptor cable that is shown in immage below. I have used such cables to upgrade my PC with new HDD SADA disk of higher capacity.
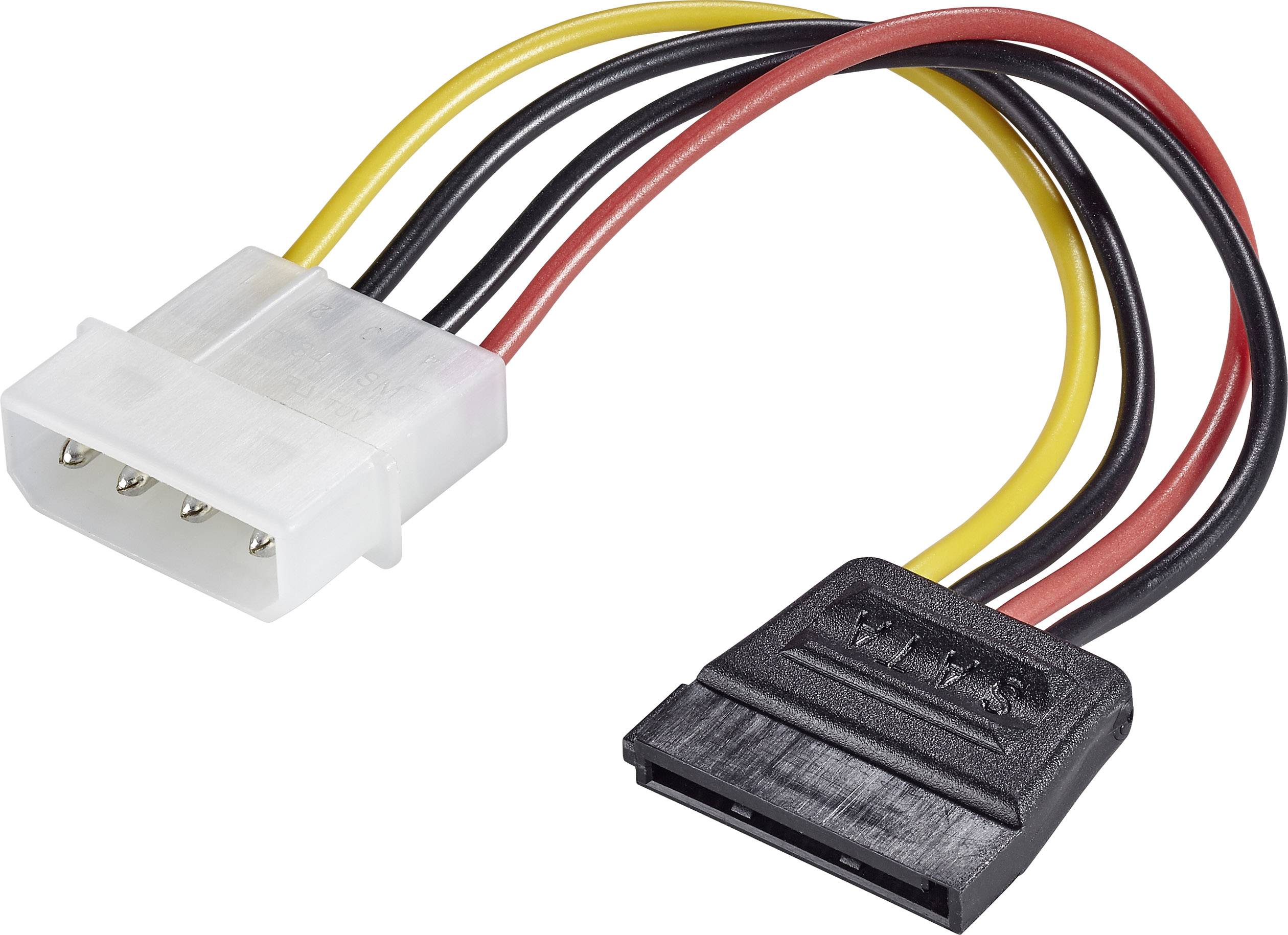

MOLEX-SATA Addaptor
For more information on HDD connectors, please visit the following websites:
What is RAID?
RAID = Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks. This is a technology used for servers to enlarge storage capacity and improve reliability quality for data storage in data centers. This technique is called RAID. There are multiple types of RAID configurations optimized for speed, safety or a balance between the two.
RAID Advantages
- Improved performance: RAID can improve performance by spreading data across multiple drives. This can help to reduce bottlenecks and improve read and write speeds.
- Increased reliability: RAID can increase reliability by providing redundancy. If one drive fails, the data can be reconstructed from the other drives.
- Enhanced capacity: RAID can also increase capacity by striping data across multiple drives. This can help to achieve a larger overall capacity than a single drive.
RAID Inconvenience
- For RAID you use several disks that can make computer more heavy;
- You need a computer case with 4 or more HDD locations to create a RAID;
- RAID consume more power then a single disk in a computer;
- You should not use SSD for any RAID other then RAID0.
RAID Type
There are 2 ways to create a RAID array:
Software RAID and hardware RAID. For hardware RAID you need a specific card that is to control several disks. New PC motherboards have support for RAID using SATA controller. Software RAID is available as a feature of the operating system. There are different RAID levels, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common RAID levels include:
- RAID 0: This is the simplest RAID level and provides no redundancy. However, it can improve performance by striping data across multiple drives.
- RAID 1: This provides complete redundancy by mirroring data across two drives. This is the most reliable RAID level, but it also has the lowest capacity.
- RAID 5: This provides a good balance of performance and reliability by striping data across multiple drives and using parity to protect data.
The best RAID level for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements. If you are looking for the best possible performance, then RAID 0 may be a good option. If you need the most reliable RAID level, then RAID 1 may be a better choice. If you are looking for a good balance of performance and reliability, then RAID 5 may be the best option for you.
RAID Parameters
There are 2 important parameters you have to consider when you decide what kind of RAID to create:
- CHUNK SIZE
- RAID LEVEL
CHUNK SIZE
To get good performance you must have a reasonable chunk size specific to your work or job.
For video editing: You want a lot of bandwidth, so you want a small chunk size. Anywhere from 512 bytes (one block) to 8 KB is a small chunk size. This will allow multiple disks to contribute to data stream at once increasing the data bandwidth.
For a database: You want to maximize your IOPS, which ideally means sending each I/O to only one disk. So you want a large chunk size – at least 64 KB or more. That large chunk will mean that most I/Os get serviced by a single disk and more I/Os are available on the remaining disks.
RAID LEVELS
RAID capacity, performance and reliability are in balance. Depending on your goal one kind of RAID is better then another. Here are the most important RAID flavors:
JBOD: Just a bunch of disks. is known as "spanned volume" on Windows. It is the best choice for a desktop PC. It increase the size of the volume and keep the performance at maximum. This is the most suitable RAID for a beginner who has too many disks in his computer.
RAID-0: Known as "striped volume" on Windows. RAID-0 is good for speed, you can use two or more hard drives.The storage capacity grow linear with the number of drives. On Linux RAID-0 can be created using MD-RAID, LVM or BtrFS.

RAID-O diagram
The major limitation of RAID-0 compared to other RAID levels is that does not offer any redundancy. RAID-0 can be used to increase storage capacity, sequential read and sequential write.
RAID-1: Known as "mirrored volume" for Windows, RAID-1 is good for data safety and it increase the reading speed but you can use only 2 hard drives. RAID-1 offer 100% redundancy but will not increase your writing speed or disk space.
This is available only on Windows professional edition and Windows server edition. It is not available on Windows home edition.

RAID 1 diagram
Note: RAID chunk size do not have effect on performance for RAID 1.
RAID-5: is using 3 or more hard drives and has a special algorithm to distribute data across these disks. If one of the disk fail it can be replaced and array is rebuild by the system. The tricky part is to know which hard disk has failed. If you replace the wrong hard drive you will probably loose all the data.

RAID 5 diagram
RAID 6: is using 4 or more hard drives and is using double redundancy. So if any disk fail you can replace the disk but if you replace the wrong disk data is not lost. This RAID is using some more processing power to write and read from the HDD due to redundancy algorithm. This is the most used RAID in enterprise class NAS or server storage.
RAID-10 A server need minimum 4 disks to create RAID-10. The speed for write will be up to 2x faster then a single disk while the speed for reading is 4x faster. RAID-10 can use 4, 6 or 8 HDD for storing videos and pictures. RAID-10 is not good for servers.

RAID 10 diagram
RAID combination
Enterprise servers are using RAID-6, however combinations of RAID-6 and STRIP can create larger had drive arrays that are faster than RAID-6 by using RAID-60. You can find schema for different kind of combinations on the interned. Important to know is that it can be done.
Spare disks
Some RAID arrays have support for one or more spare disks. These disks do not have data but they are in reserve. If one of disks fail, the RAID is able to repair itself, disabling the defect disk automatically and rebuilding the array on the fly. This is a professional solution and is used frequent on critical servers.
Personal RAID
Personal computer sometimes enable RAID but most of the time a desktop computer has one single hard disk. If you use two disks then one is for operating system one is for backup. If you have 4 disks then you can use different size disks or same size disks.
First disk is for Windows System, and it can be SSD. Second disk is of large capacity and is for Backup. Disks 3 & 4 can be same size and connected in RAID-1. Do not ever use RAID-0 on a PC it is dangerous to loose data. The RAID 0 can break easy on a desktop computer if you sue SATA disks. On server there is a different class of hard-disks: Enterprise Class, made express for RAID. If you purchase this kind of disks you can have RAID at home.
What is NAS?
A NAS storage is an external box having several HDD installed in RAID. It is in fact a computer that is dedicated for large storage capacity. It can connect using a e-sata cable (external SATA) or fiber optics. In the next picture you can see an example of NAS storage. Feel free to investigate careful for your NAS or external drive solution before you buy. This is not for everyone but it can be useful for a small office to make backups on it or to store a large database.

External NAS micro server
Server / NAS RAID storage
RAID is usually required for servers. In the picture below we show you a RAC with several disks that are mounted. Each disk can be extracted easy without any tool. The drivers are installed in special drawers that have ventilation and a special handle that will disconnect the diver and then you can pull the driver out while the server is running.
Of course you must have a good reason to pull out a disk or an entire array. Usually a defect disk has a red light that indicate is defect and must be changed. If does not then you can measure temperature of disk and if one gets hot then it must be changed. Of course this id difficult if the drawer do not have a thermometer on it.

Enterprise NAS RACK
Read next: Backup
