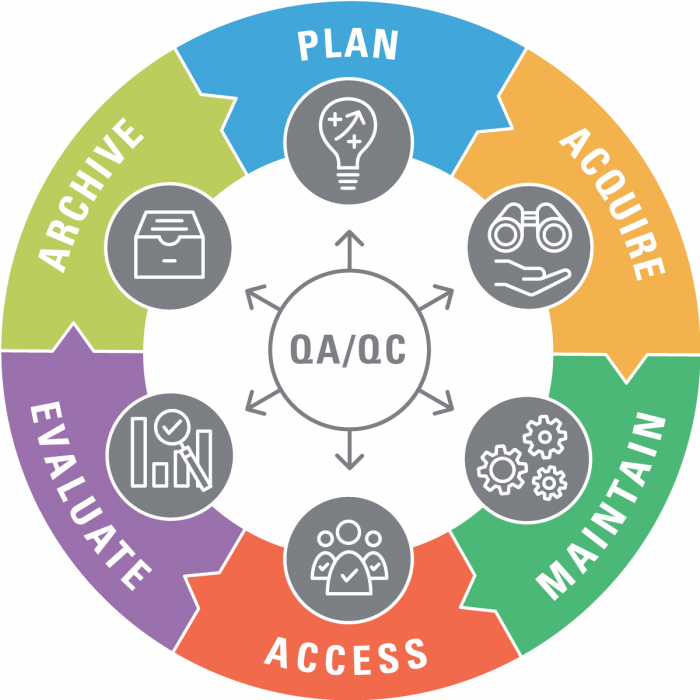
Data Life Cycle
DLC Stages
Data life cicle can be organized in a cyclic workflow. Data must be created or collected then it must be cleaned and stored. We may reorganize data in many ways to make data available for ussage and analyze the data or publish then maybe we archive the data or even remove the old data and collect new data. Here are the details for each step:
Domain of DS
- Data Creation: Data is created through various sources like customer forms, website traffic data, sensor readings, social media posts, etc.
- Data Collection: The created data is collected and stored in databases, data warehouses or data lakes.
- Data Processing: The collected data is cleaned, transformed and organized into a usable format. Data quality checks are performed.
- Data Analysis: The processed data is analyzed using tools like SQL, business intelligence software and data science techniques.
- Data Visualization: Insights from the data analysis are visualized using dashboards, reports, charts and graphs.
- Data Application: The visualized data and insights are applied to improve products, optimize processes, inform decisions and gain a competitive advantage.
- Data Retention: Relevant data is retained according to compliance and business needs. Irrelevant data is deleted.
- Data Archiving: Non-critical but relevant data is moved to cheaper storage for long-term retention. It is kept offline but can be retrieved if needed.
- Data Disposal: Obsolete data that is no longer needed is securely deleted from all systems and storage media.
DLC Strategies
There are different strategies organizations can follow for the data life cycle:
- Active data life cycle: In this strategy, data remains active and usable for as long as needed. There are no predetermined retention or disposal periods. Data is retained as long as it is useful and relevant. This strategy is suitable for data that is continuously accessed and updated.
- Scheduled data life cycle: In this strategy, data is retained for a predetermined period based on business and regulatory needs. After that retention period, data is either archived or disposed of. This helps manage data growth and ensure compliance.
- Event-driven data life cycle: In this strategy, data retention and disposal is triggered by specific events. For example, data related to a customer may be retained until the customer leaves the company. Then the data is disposed of.
- Hierarchical data life cycle: Different retention and disposal periods are set for different types of data within an organization. More critical data is retained for longer while less important data has shorter retention periods.
The data life cycle strategy an organization chooses depends on its specific needs, compliance requirements, data usage patterns and resources. The goal is to retain data as long as necessary while disposing of data that is no longer needed in an efficient manner.
Data Collection
There are many different sources and methods for collecting and creating data. Some of the most common sources include:
- Sensors
- Log files
- Surveys
- Transactional data
- Social media data
Some of the most common methods for collecting and creating data include:
- Manual entry
- Automatic capture
- Web scraping
- Data mining
- Machine learning
The choice of source and method for collecting and creating data will depend on the specific needs of the project. For example, if you are collecting data about sensor readings, you will need to use a different source and method than if you are collecting data about social media posts.
The data collection and creation stage is an important part of the data life cycle. It is important to choose the right sources and methods to ensure that you collect the data you need in a way that is efficient and accurate.
Data Processing
Data processing is the process of transforming raw data into a format that is more useful for analysis. This can involve cleaning the data, removing outliers, and formatting it in a way that is easy to understand.
Data processing is an important part of the data science process. It is the first step in making sense of data and identifying patterns that can be used to make predictions or decisions.
There are many different tools and techniques that can be used for data processing. Some of the most common include:
- Data cleaning
- Data transformation
- Data integration
- Data mining
- Machine learning
The choice of tool or technique for data processing will depend on the specific needs of the project. For example, if the data is dirty, then data cleaning tools will be needed. If the data needs to be transformed into a different format, then data transformation tools will be needed.
Data processing is a complex and challenging task. However, it is an essential part of the data science process. By carefully processing data, data scientists can make sense of it and identify patterns that can be used to make predictions or decisions.
Data Analysis
Data analysis is the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making.
Data analysis is an important part of the data science process. It is the process of making sense of data and identifying patterns that can be used to make predictions or decisions.
There are many different tools and techniques that can be used for data analysis. Some of the most common include:
- Descriptive statistics
- Inferential statistics
- Machine learning
- Data mining
- Natural language processing
The choice of tool or technique for data analysis will depend on the specific needs of the project. For example, if you are trying to understand the distribution of data, then descriptive statistics might be a good choice. If you are trying to predict future behavior, then machine learning might be a good choice.
Data analysis is a complex and challenging task. However, it is an essential part of the data science process. By carefully analyzing data, data scientists can make sense of it and identify patterns that can be used to make predictions or decisions.
Data Visualization
Data visualization is the presentation of data in a graphical format to make it easier for people to understand. This can be done through charts, graphs, maps, and other visual representations.
Data visualization is an important part of the data science process. It can help data scientists to communicate their findings to stakeholders, identify patterns in data, and make predictions.
There are many different tools and techniques that can be used for data visualization. Some of the most common include:
- Charts
- Graphs
- Maps
- Heatmaps
- Treemaps
The choice of tool or technique for data visualization will depend on the specific needs of the project. For example, if you are trying to show the relationship between two variables, then a scatter plot might be a good choice. If you are trying to show the distribution of data, then a histogram might be a good choice.
Data visualization is a powerful tool that can help data scientists to communicate their findings and make better decisions. By carefully choosing the right visualization techniques, data scientists can make their data more understandable and accessible to others.
Data Application
Data application in data science is the process of using data to solve real-world problems. This can involve using data to make predictions, optimize processes, or improve decision-making.
Here are some examples of data applications in different industries:
- Healthcare: Data can be used to identify diseases, track patient progress, and personalize treatment plans.
- Finance: Data can be used to assess risk, make investment decisions, and prevent fraud.
- Retail: Data can be used to understand customer behavior, optimize inventory, and personalize marketing campaigns.
- Manufacturing: Data can be used to improve quality control, optimize production, and reduce costs.
- Transportation: Data can be used to improve traffic flow, optimize routes, and prevent accidents.
The choice of data application will depend on the specific problem that is being solved. For example, if a company is trying to predict customer churn, they might use a predictive modeling algorithm. If a manufacturing company is trying to identify bottlenecks in its production process, they might use a data mining algorithm.
Data application is an essential part of data science. By applying data to real-world problems, data scientists can help businesses to improve their operations, make better decisions, and ultimately achieve their goals.
Data Governance
Data governance is the practice of ensuring that data is managed in a consistent, secure, and compliant manner. It includes the policies and procedures for managing data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to disposal.
By having clear data governance policies in place, organizations can ensure that their data is stored and disposed of in a secure and compliant manner. This helps to protect the privacy of individuals, comply with regulations, and ensure the integrity of data.
Data retention, archiving, and disposal are all important aspects of data governance. Data retention refers to the length of time that data is stored. Archiving refers to the process of moving data to a long-term storage medium. Disposal refers to the process of deleting or destroying data.
Here are some other words that can be used to describe data governance:
- Data management: The overall process of managing data.
- Data stewardship: The responsibility for ensuring that data is managed in a consistent and compliant manner.
- Data administration: The day-to-day tasks of managing data, such as creating and updating data dictionaries.
- Data security: The protection of data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
- Data privacy: The right of individuals to control their personal data.
The specific word that is used will depend on the specific context. For example, a data scientist might use the term "data governance" to refer to the overall process of managing data, while a lawyer might use the term "data privacy" to refer to the specific laws and regulations that govern the collection and use of personal data.
Gouvernance Policy
There are a number of factors to consider when determining the data retention, archiving, and disposal policies for a data science project. These factors include:
- The type of data being collected
- The purpose of the data collection
- The regulatory requirements
- The cost of storage
- The risk of data breaches
The data retention policy should specify how long different types of data will be stored. For example, data that is used for compliance purposes may need to be stored for a longer period of time than data that is used for marketing purposes.
The archiving policy should specify how data will be migrated to a long-term storage medium. The archiving process should ensure that the data is secure and accessible.
The disposal policy should specify how data will be deleted or destroyed. The disposal process should ensure that the data is irretrievable.
Data Security
Data security is a critical aspect of any data science project. It involves protecting data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, inspection, recording or destruction.
Here are some of the key data security considerations for data scientists:
- Secure data storage: Sensitive data should be stored in encrypted databases, file systems and data warehouses. Data should also be segmented based on sensitivity and access requirements.
- Secure data transmission: Data transmitted between systems and applications should be encrypted in transit using TLS/SSL or VPNs.
- Access controls: Role-based access controls should be implemented to limit data access to only authorized personnel. Credentials should be strong and rotated periodically.
- Anonymization: Personally identifiable information should be anonymized where possible to reduce security and privacy risks.
- Secure data labeling: Any data used for training models should be properly labeled and classified to avoid introducing biases.
- Secure model development: Models should be tested for bias, fairness and robustness before deployment in production.
- Secure data deletion: Any data no longer needed should be securely wiped from all systems to prevent retrieval and reconstruction.
- Secure data visualization: Visualizations should avoid showing granular data that could reveal sensitive insights.
Data security needs to be a part of the entire data science life cycle from data collection and storage to model deployment and data deletion. With the proper security measures, data scientists can unlock insights from data while minimizing risks.
Read next: Collecting Data
